This text is featured in Bitcoin Journal’s “The Inscription Difficulty”. Click on right here to get your Annual Bitcoin Journal Subscription.
Click on right here to obtain a PDF of this text.
Ordinals have been a polarizing phenomenon for many each subcommunity in Bitcoin — apart from miners.
The meteoric rise of the brand new Bitcoin-native NFT customary dominated discourse for months as Ordinals flooded blockspace and buoyed transaction charges to multiyear highs. Based on critics, these transactions are, at worst, an assault on Bitcoin that tainted the sanctity of scarce blockspace; at greatest, they’re shitcoins, the play-things of gamblers that belong on on line casino chains like Ethereum.
Effectively, miners don’t give a shit in the event that they’re shitcoins. They provide a shit about earning money, and Ordinals gave them a income enhance at a time when mining earnings was at considered one of its lowest factors ever. So many miners have embraced — or as a minimum, are ambivalent about — Ordinals/inscriptions, since they obtained a much-needed enhance to Bitcoin mining profitability when many miners had been practically breakeven or unprofitable.
Hashprice is a measure of the USD (or BTC) quantity miners can anticipate to earn from a unit of hashrate (for instance, at $80/PH/day, a miner with 1 petahash of mining rigs — roughly 10 new-gen ASICs just like the S19j Professional, for instance — can earn $80 per day).
Given their optimistic influence on hashprice, Ordinals, a darkhorse technical development that few may have predicted final 12 months, have discovered themselves on the middle of discussions concerning Bitcoin mining economics, discussions which can be extra germane with every block that pulls us nearer to Bitcoin’s fourth block subsidy halving.

I’m not penning this to proselytize anybody into changing into an Ordinals enjoooyer. I, for one, don’t actually perceive the attraction. However I do assume that they’re essential within the context of Bitcoin’s ever-dwindling block subsidy, so that they’re price learning to know how they have an effect on blockspace and mining economics — and what developments like them may imply in a future the place miners subsist solely on transaction charges.
WTF is an Ordinal, Anyway?
In NFT parlance, of us use Ordinal and inscription interchangeably, however the person phrases refer to 2 completely different elements of the NFT customary.
An inscription is a chunk of artwork or digital media, whereas an Ordinal is technically the quantity prescribed to an inscription to mark its place within the grand scheme of all different inscriptions. One other method to view it’s that the inscription itself is the NFT, whereas the Ordinal is the quantity used to determine a person inscription.
The info for every inscription lives within the Segregated Witness part of a transaction. As such, not like different NFT requirements, the precise artwork, digital media, or information is uploaded on to Bitcoin’s blockchain. Because the inscriptions are totally on-chain, you possibly can argue that they’re the purest type of NFT accessible as they profit from the blockchain’s immutability.
Not All Inscriptions Are Created Equal
While you perceive that inscriptions are precise on-chain information, you’ll be able to recognize among the critiques and issues from detractors; if a bunch of NFT degens are inscribing monkey JPEGs and dickbutts and God-knows-what-else on-chain, then this crowds out financial (and probably essential) transactions.
This concern was aggravated by the truth that the arbitrary information for every inscription advantages from a transaction payment low cost. As a scalability measure, Bitcoin’s Segregated Witness improve modified the transaction construction in order that the witness information for a non-public key signature and public key was moved from the transaction hash discipline to a different a part of the block. Bitcoin reductions SegWit information, so it requires fewer satoshis per byte in transaction charges to transact. The arbitrary information for an inscription lives within the SegWit discipline of a transaction, so it’s entitled to the SegWit low cost. Cue the pitchforks.
This low cost is why, regardless of the primary wave of image-based inscriptions clogging block house in February/March/April, transaction charges didn’t meaningfully enhance; block sizes swelled when trendsetting inscribers flushed the blockchain with 1000’s of JPEGs for the primary inscriptions collections, however these all benefited from SegWit’s 4-to-1 information low cost versus regular transactions. Maybe intuitively, it wasn’t till much less data-heavy, text-based inscriptions from BRC-20 tokens grew to become the most well-liked inscription sort that transaction charges soared.
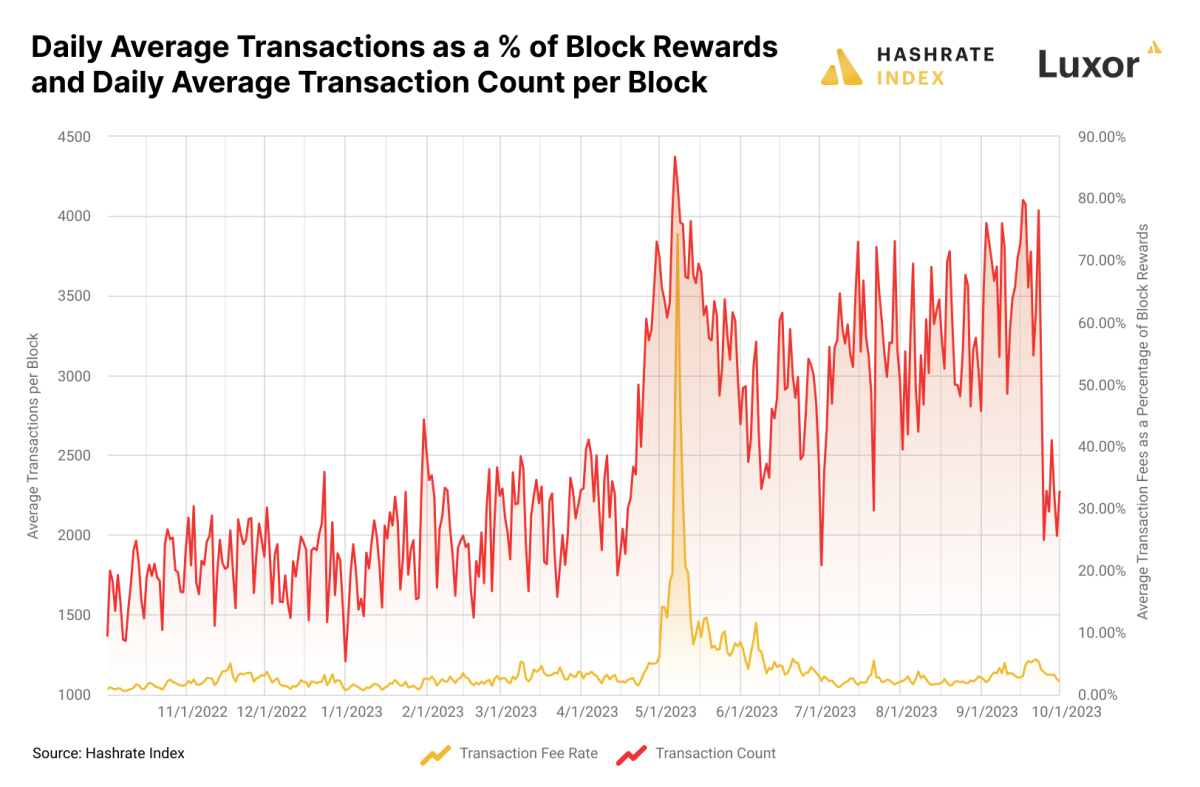
So-called BRC-20s (a nod to Ethereum’s personal ERC-20 token customary) are a unfastened type of token. I say unfastened as a result of they’re actually simply Ordinals in a sequence outlined by Bitcoin’s OP_CODE operate, the place every “token” is itself an OP_CODE transaction that defines the token’s place within the particular BRC-20 sequence. It goes like this: Somebody (God solely is aware of who) publishes an OP_CODE transaction that defines the token sequence’ max provide, ticker, and the minting restrict per transaction. As soon as publicized, anybody with the technical know-how can mint tokens within the sequence.
These OP_CODE transactions don’t profit from SegWit’s information low cost, so that they price a reasonably penny greater than image-based inscriptions. However in addition they have a characteristic that picture inscriptions don’t: the minting operate, which brings Ethereum NFT-esque incentives to gathering these inscriptions. Ethereum NFT sequence usually have minting contracts the place anybody can create new NFTs within the sequence by interacting with the contract. That is a part of — if not all the — attraction. Minting an NFT is like opening up a digital pack of Pokémon/baseball/Magic: The Gathering playing cards — possibly there’s a uncommon card on this subsequent one!
And whereas there isn’t essentially the chance to mint a uncommon BRC-20 (as a result of they’re all the identical), there’s the possibility to mint a bunch of NFTs in a sizzling new sequence. Why anybody cares about having ORDI/CUMY/RATS #1 or #100 or no matter, I don’t know. Maybe it’s the best expression of the larger idiot principle but in Bitcoin. However the reality is, they do, and the minting incentives for BRC-20s precipitated the biggest wave of Bitcoin transaction exercise ever.
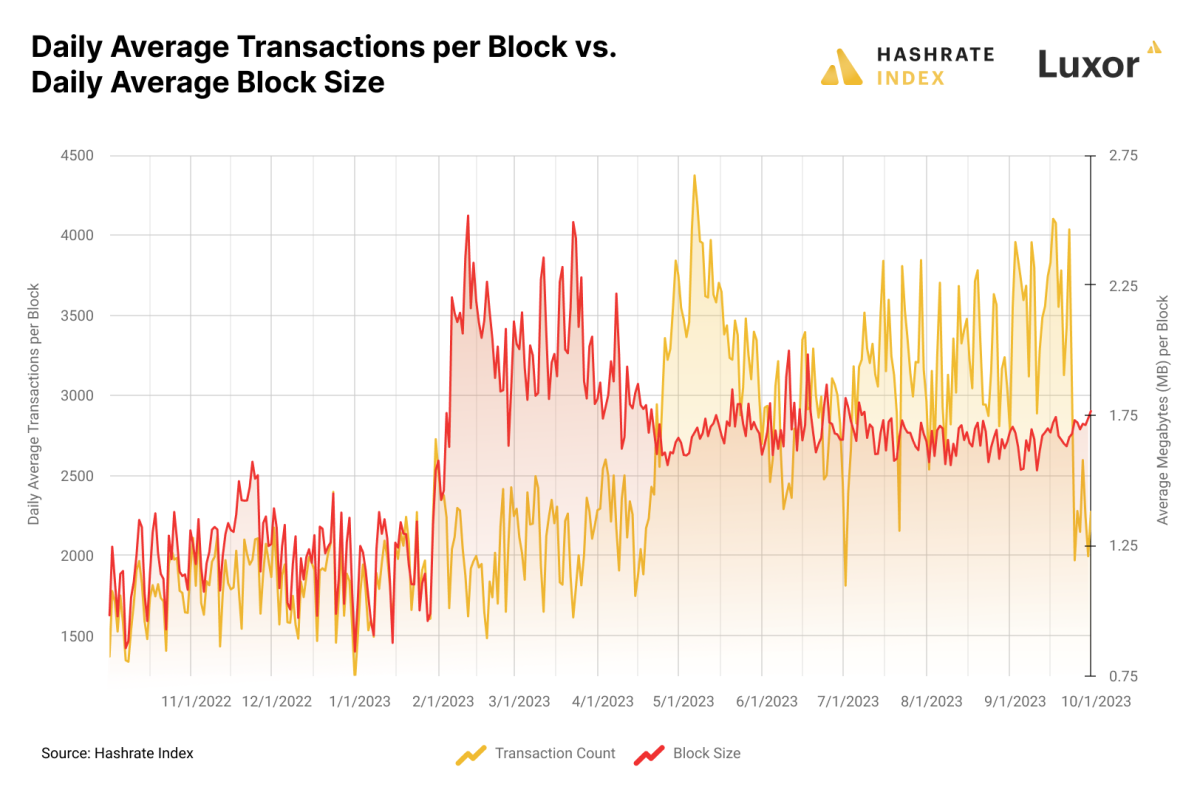
By a mixture of payment wars and the truth that these NFTs don’t profit from the SegWit low cost, BRC-20s have catered a veritable payment feast for Bitcoin miners, however not precisely in the way in which you may assume.
Quantifying Transaction Charge Collateral Injury
The majority of transaction payment will increase in 2023 has not come instantly from charges related to Ordinals; it has come from oblique payment strain on different transactions.
Per information from unbiased analyst Information All the time’ Dune dashboard, as of November 12, 2023, miners have raked in $70.3 million charges from Ordinals. Appears bigly, nevertheless it’s solely 19.4% of the $368.2 million in transaction charges that miners have earned in whole since inscriptions debuted on December 14, 2022. To place this into additional perspective, there have been 40.2 million inscription transactions, which equates to 30% of all transaction quantity since December 14. So inscriptions have accounted for one-third of transaction quantity over the past 12 months however solely one-fifth of all charges.

As for the opposite charges, lots of them are the results of oblique payment strain from inscriptions — that’s, charges that don’t come instantly from inscriptions themselves, however from the strain that inscriptions exert on the common transaction payment wanted to clear a Bitcoin transaction in an inexpensive timeframe.
Galaxy Digital Analysis examines this dynamic in a report titled “Bitcoin Inscriptions & Ordinals: A Maturing Ecosystem”. Rampant inscription exercise congests the mempool. That is notably true throughout BRC-20 minting occasions, because the first-come-first-mint incentivizes bidding wars as inscribers gun to be the primary to mint a sequence. This raises the ground for common transaction charges and, as Galaxy Digital Analysis factors out, precipitates transaction payment “overpayment” from numerous transactors. They outline overpayment as any payment in a block that’s larger than that block’s median transaction payment. For regular transactions, this overpayment may come from transaction payment estimators in wallets or on exchanges or from common consumer ignorance concerning transaction payment construction and dynamics. Some customers might also have to expedite transactions for any variety of causes, resulting in overpayment. For inscription transactions, Galaxy Digital Analysis says that “voluntary overpayment” was commonplace throughout occasions of excessive exercise and common inscription mints.
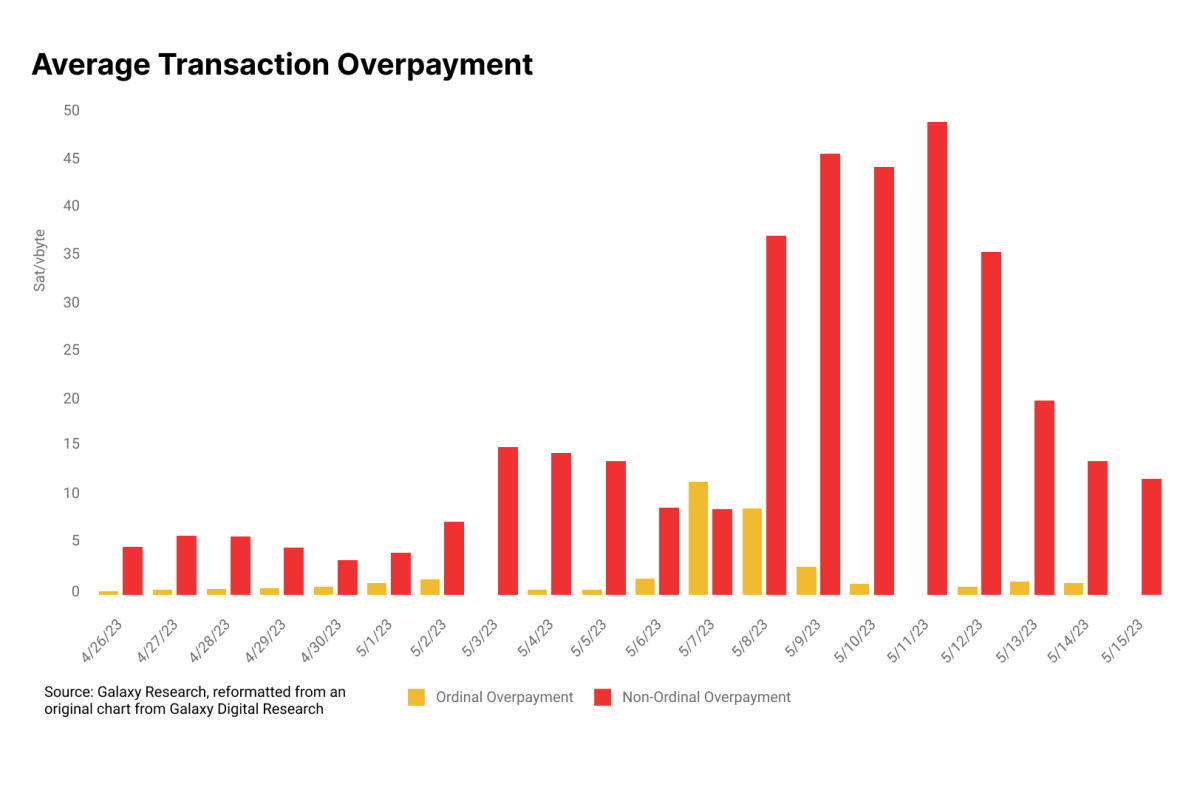
This chart quantifies overpayment for inscription transactions and all different transactions to exhibit the dynamics Galaxy Digital Analysis outlines of their report. When Bitcoin’s mempool grew to become backlogged in April and Might — the most popular timeframe for inscription exercise up to now — a majority of the transaction charges throughout this time truly got here from consumer overpayment for monetary transactions, not inscriptions themselves. These customers may most likely make it simpler on themselves by not utilizing built-in transaction payment estimators with their wallets and exchanges.
Blessing and a Curse
Inscriptions are a blessing and a curse. They’re a godsend for miners, however they could be a ache within the ass for different Bitcoiners, notably those that need to ship transactions on the community every single day.
That mentioned, blockspace is an open market. So I don’t have to love Ordinals to acknowledge that it’s not my place to police another person’s spending. Neither is it my place to censor a transaction that pays for blockspace on the f(r)ee market. That’s a part of the purpose of a permissionless blockchain, in any case: to make transactions different folks don’t need you to make.
This text is featured in Bitcoin Journal’s “The Inscription Difficulty”. Click on right here to get your Annual Bitcoin Journal Subscription.
Click on right here to obtain a PDF of this text.